Weeds are often referred to as “nuisance plants”, and can be a nuisance in gardens and yards but they can also be dangerous. Many weeds are poisonous and can cause serious health problems if ingested or in contact with humans or animals. It is important to understand which weeds may cause harm and how to protect yourself and your family from them.
Weeds are often seen as nothing more than nuisances in gardens and yards, but some weeds can actually be poisonous to humans. In this guide, we will explore the most common poisonous weeds found in America and the UK.
In this blog, we discuss the symptoms and dangers of ingesting or coming into contact with these plants.
Common Poisonous Weeds
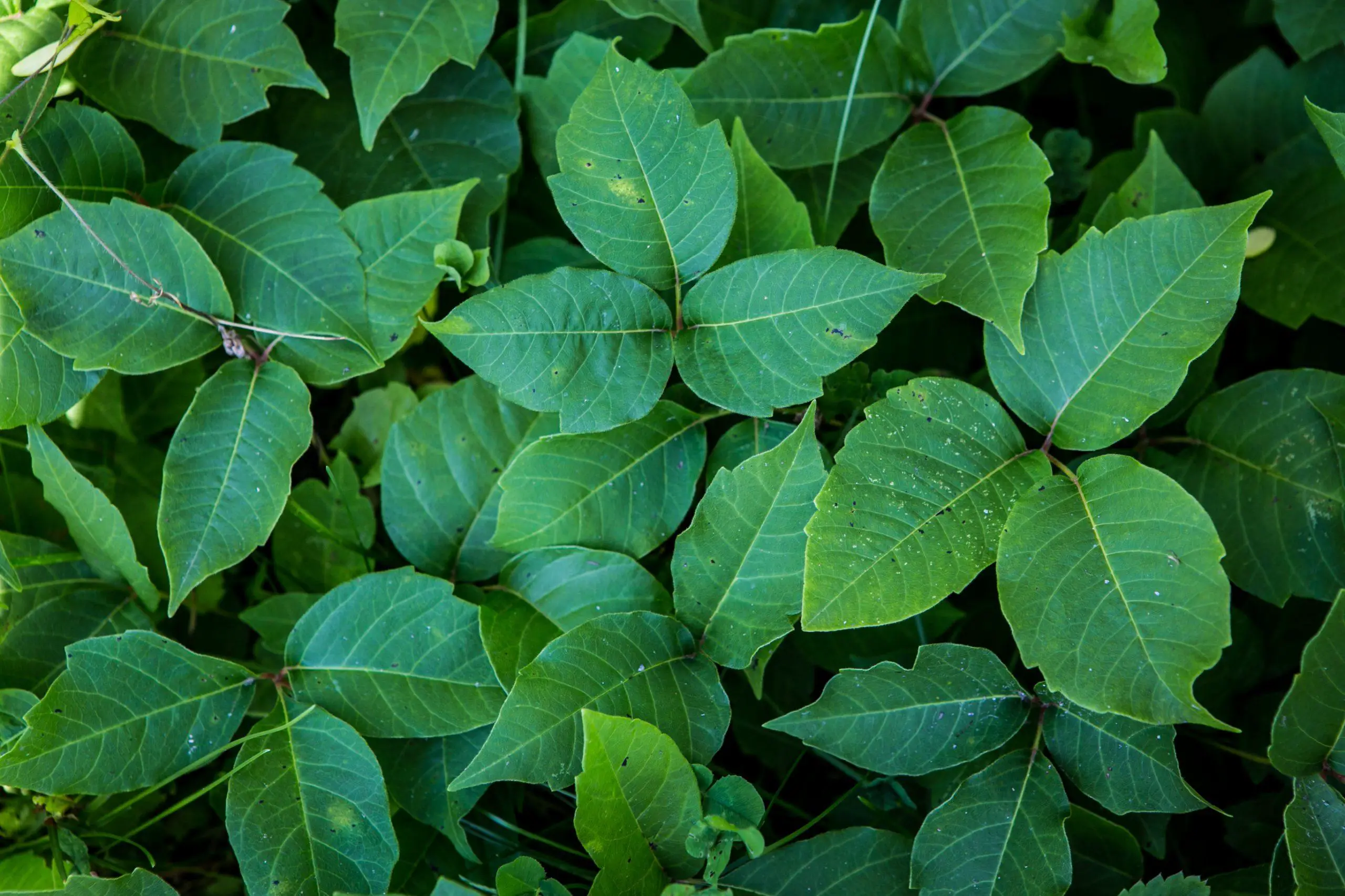

Poison Ivy
Poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans) is a common poisonous plant that can cause an itchy and sometimes painful rash in humans who come into contact with it. The rash is caused by an oil called urushiol, which is found in the leaves, stem, and roots of the plant. When the oil comes into contact with the skin, it causes an allergic reaction, resulting in the characteristic symptoms of poison ivy exposure.
Urushiol is a complex mixture of organic compounds that can be found in the leaves and other parts of the poison ivy plant. The oil is released when the plant is bruised or damaged in any way, and it can adhere to anything that it comes into contact with, including clothing, tools, and pets. When someone comes into contact with urushiol, it binds to the skin and begins to cause an allergic reaction.
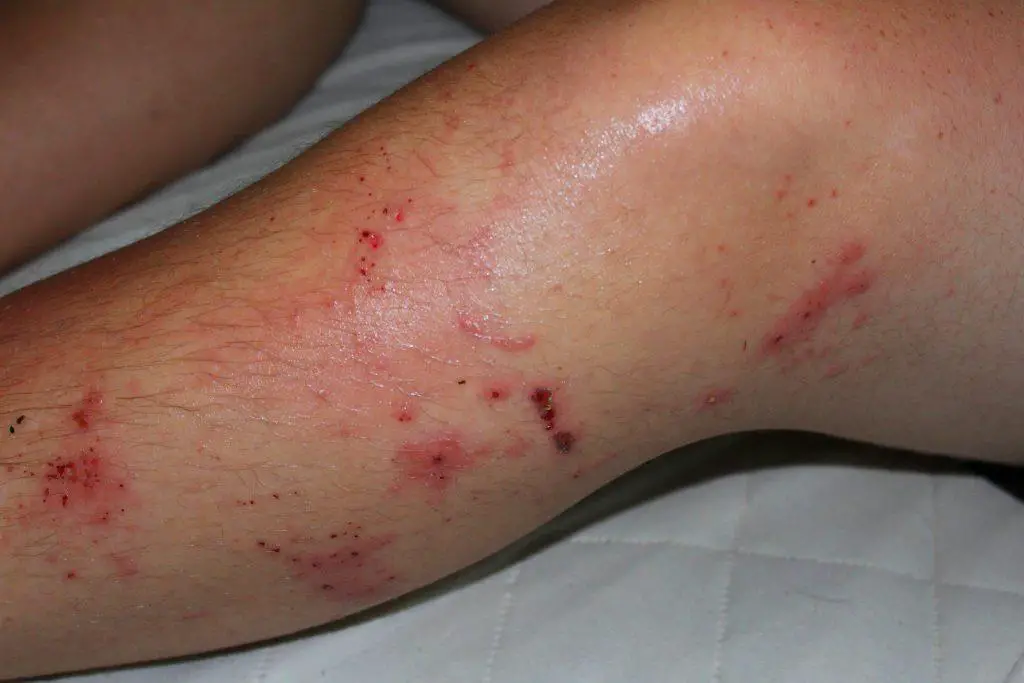
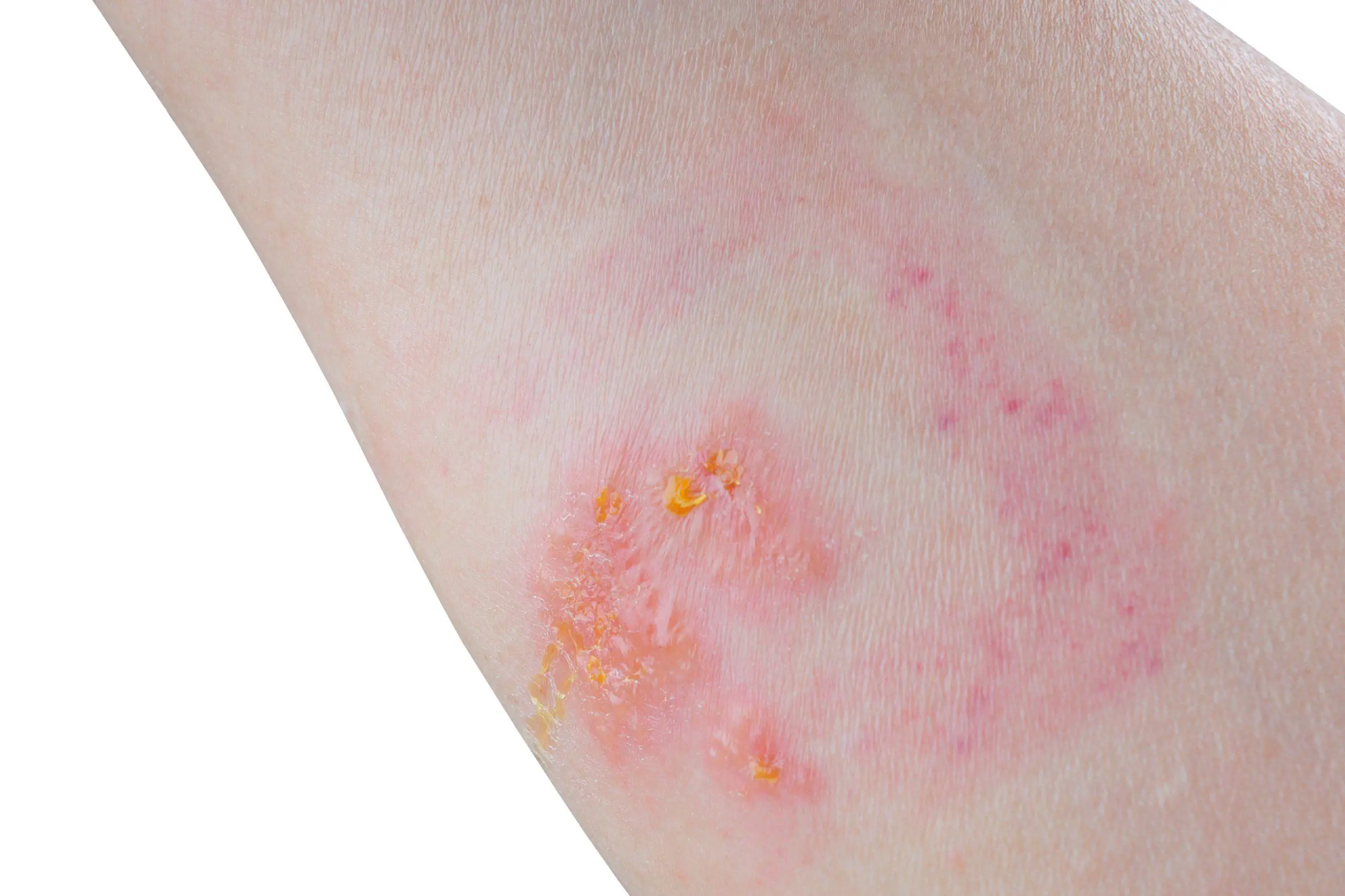
The symptoms of poison ivy exposure typically appear within 12 to 48 hours after contact and include itching, redness, and swelling of the affected skin. In severe cases, blisters may also form. The rash can spread by touching the affected area or by coming into contact with objects or surfaces that have been contaminated with urushiol.
It’s important to note that not everyone will develop a rash after coming into contact with poison ivy. Some people may be more susceptible to the effects of urushiol than others. It’s also possible to develop a sensitivity to the oil over time so that even a small amount of contact can lead to a severe reaction.
The best way to avoid a reaction to poison ivy is to learn to identify the plant and avoid coming into contact with it. If you do come into contact with the plant, it’s important to wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and water as soon as possible to remove as much of the oil as possible. If you develop a rash or other symptoms, you can try using over-the-counter creams and lotions to relieve itching and inflammation or seek medical treatment if symptoms are severe or if you have breathing difficulties.
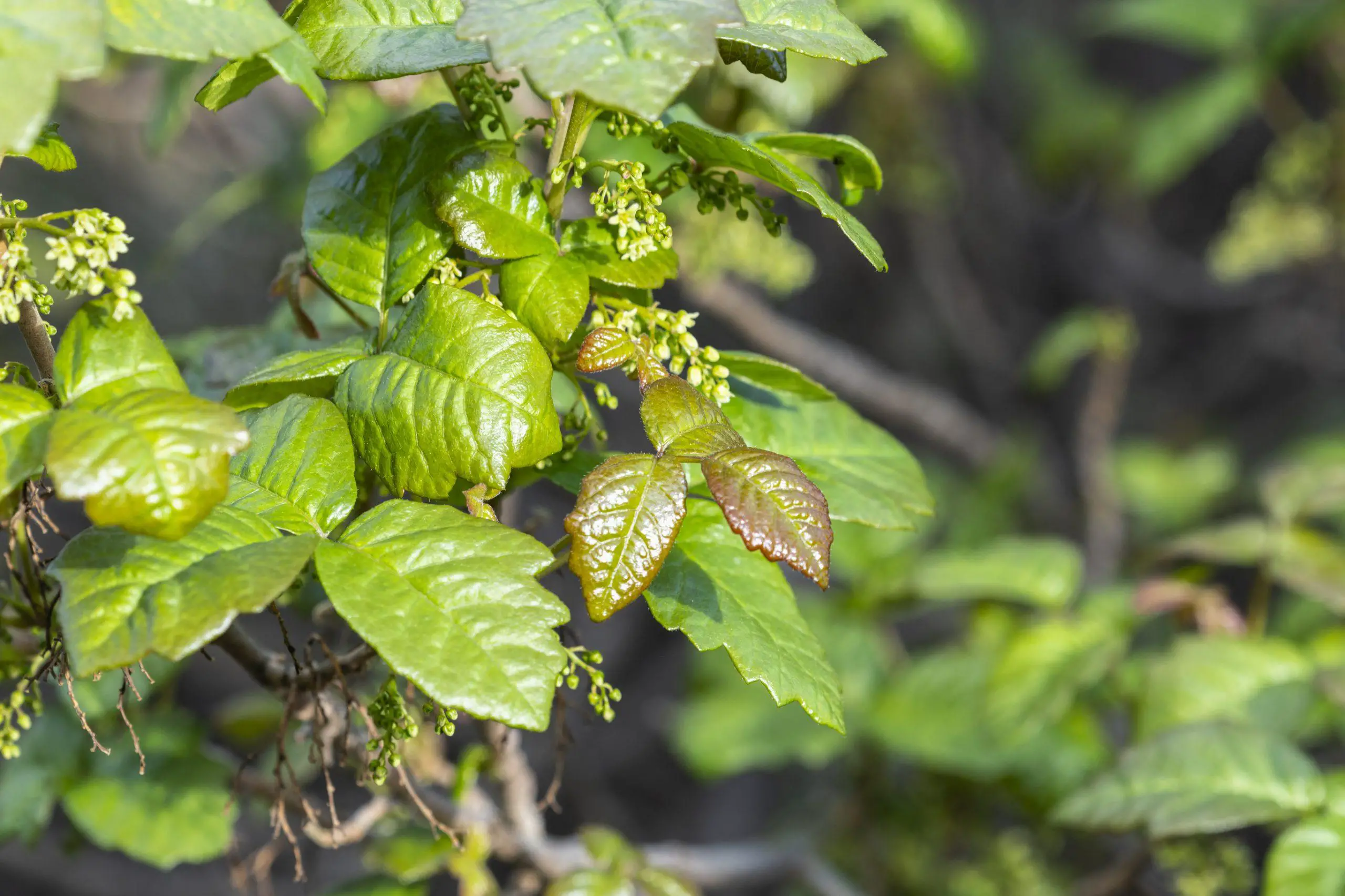

Poison Oak
Poison oak is a poisonous plant that can cause an allergic skin reaction in many people when they come into contact with its leaves, stems, or roots. The toxic compound in poison oak that causes this reaction is called urushiol, which is a clear liquid compound found in the plant’s sap.
When poison oak is touched or brushed against, urushiol can be released from the plant and transferred to the skin. Once on the skin, the urushiol begins to penetrate the skin cells, causing an immune response. The body’s immune system then produces histamine and other inflammatory chemicals, which lead to the characteristic symptoms of poison oak: itching, redness, and blistering.
Symptoms typically appear within 8-48 hours after contact with the plant and can last for one to four weeks. The rash itself can be quite severe and may spread to areas of the body not directly in contact with the plant. Scratching the rash can cause it to spread and can also lead to secondary infections.
The severity of the reaction to poison oak can vary depending on an individual’s sensitivity to urushiol, as well as the amount of the compound that comes into contact with the skin. Some people may have only a mild reaction, while others may have a severe, even life-threatening reaction. People who are more sensitive to urushiol can develop more severe reactions with less exposure to the plant.
To prevent an allergic reaction to poison oak, it is important to avoid contact with the plant. If you know you have come into contact with poison oak, wash the affected area with soap and water as soon as possible. It is important to act quickly, as washing within the first hour after contact with the plant can significantly reduce the severity of the reaction. Over-the-counter calamine lotion or hydrocortisone cream can be applied to the affected area to relieve itching, and oral antihistamines can also be helpful for severe itching.
In severe cases, prescribed medication such as oral corticosteroids may be necessary. It is important to seek medical attention if you develop difficulty breathing, fever, or swollen eyes as these can be signs of a severe reaction.
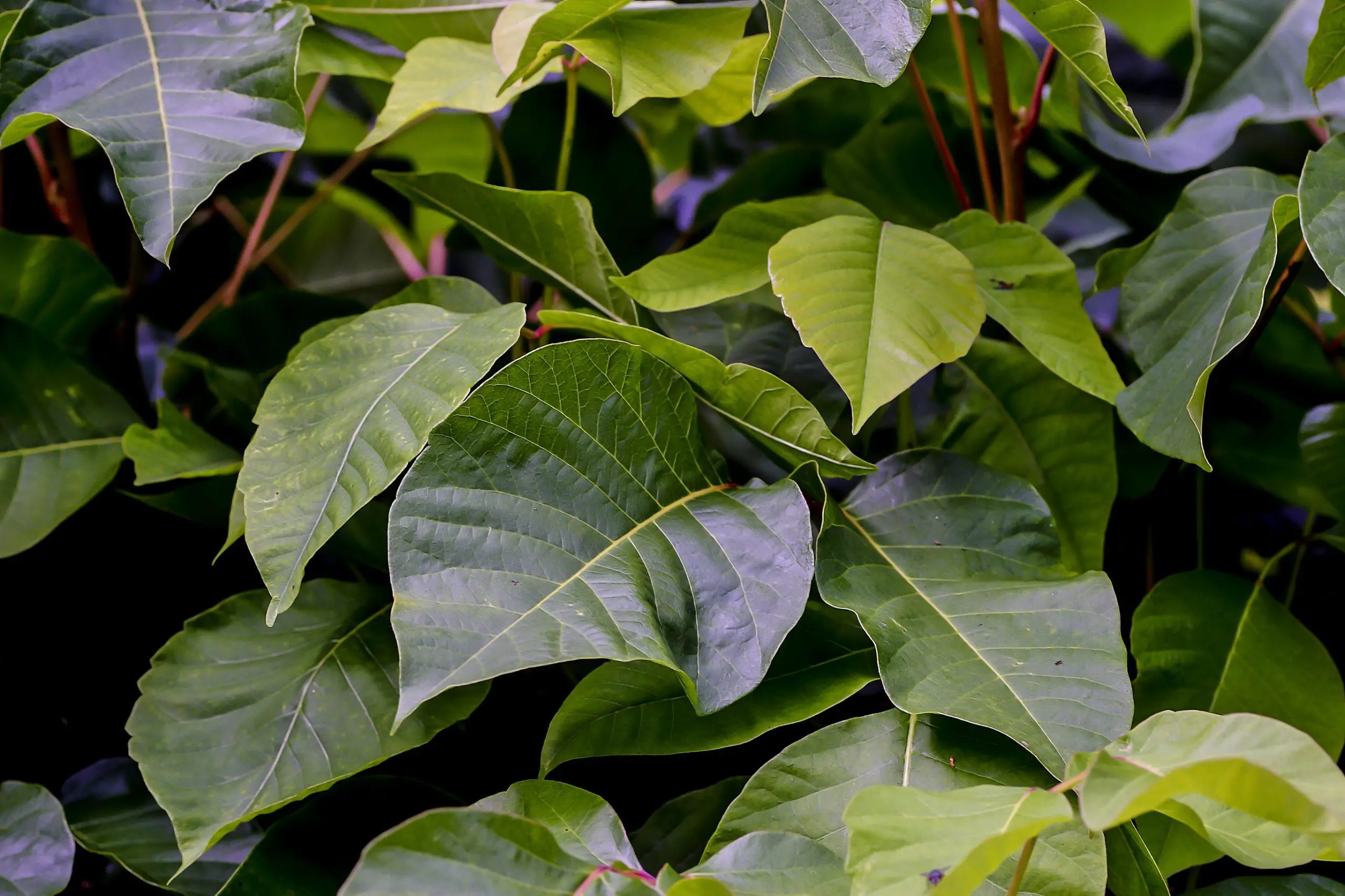

Poison Sumac
Poison sumac, which is also known as Toxicodendron vernix, is a woody shrub or small tree that is native to eastern North America. It is highly toxic to humans and can cause a severe allergic reaction known as allergic contact dermatitis.
The toxic compound in poison sumac is called urushiol, which is a type of oil found in the plant’s leaves, stems, and roots. When the plant is bruised or damaged, the urushiol is released and can come into contact with the skin. If the oil is not washed off within a short period of time, it can penetrate the skin and cause an allergic reaction.
Symptoms of poison sumac exposure typically appear within 12-48 hours after contact and can include severe itching, redness, and blistering of the skin. In severe cases, the reaction can also cause fever, headache, and swollen lymph nodes.
It’s important to note that the urushiol oil can also be spread by animals and tools, so it’s possible to come into contact with the oil even if you’ve never been near the plant itself. Additionally, the oil can remain active for up to 5 years, so even dried plant material can cause a reaction.
If you suspect that you have come into contact with poison sumac, it’s important to wash the affected area of skin thoroughly with soap and water as soon as possible. Over-the-counter antihistamines and hydrocortisone cream can also be used to relieve symptoms. In severe cases, a visit to the doctor may be required and they might prescribe oral steroids to bring down the inflammation.
To prevent exposure to poison sumac, it’s important to be familiar with the plant and to take precautions when working or recreating in areas where it may be present. Wearing protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, and gloves, can help to prevent contact with the plant’s toxic oil.
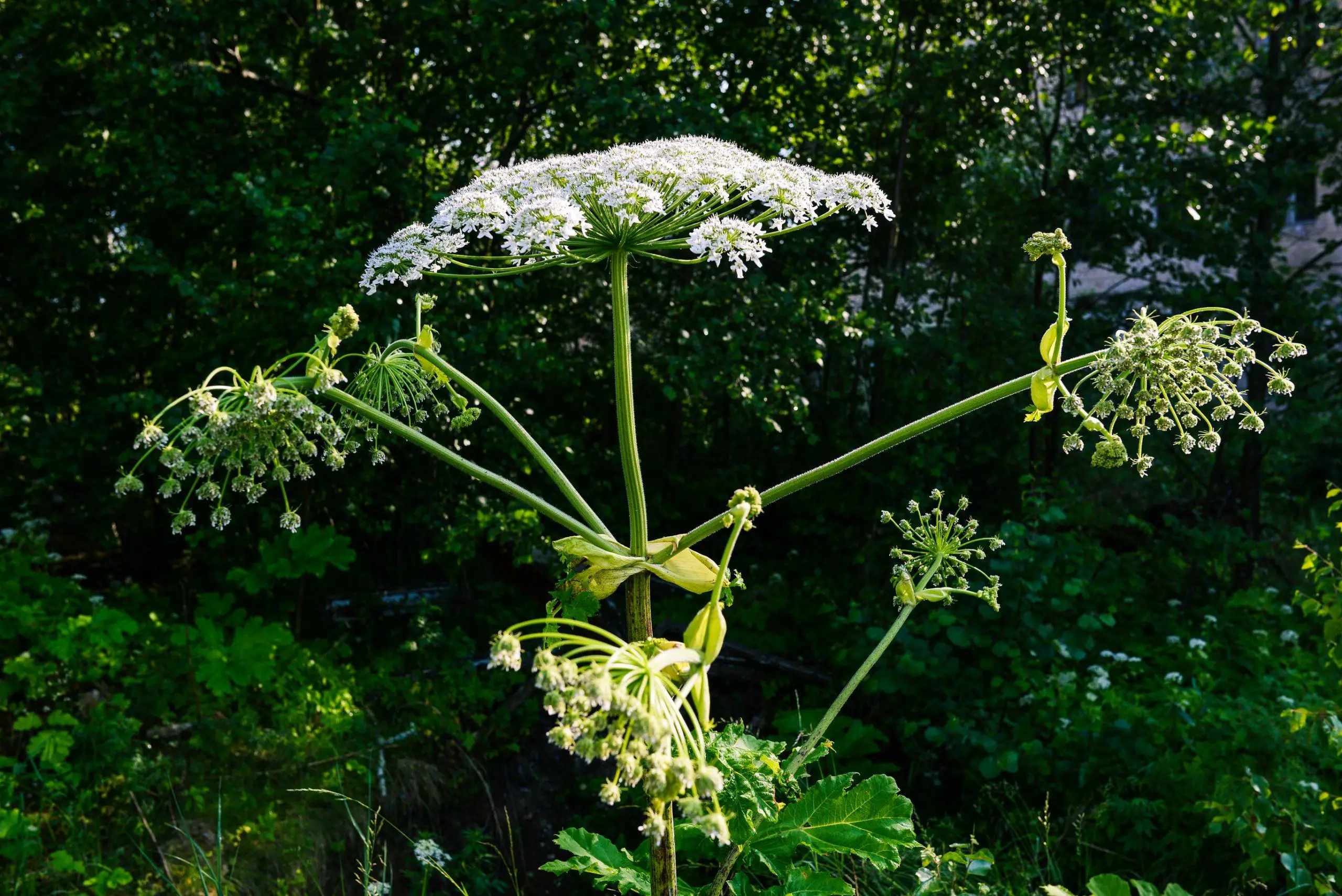

Giant Hogweed
Giant hogweed (Heracleum mantegazzianum) is a large, invasive plant species that is toxic to humans. The sap of the plant contains toxic compounds, including photosensitizing furanocoumarins, which can cause severe skin and eye irritation, blistering, and even permanent scarring.
When the sap of giant hogweed comes into contact with the skin, it reacts with UV light to cause phytophotodermatitis. This is a condition in which the skin becomes extremely sensitive to UV light, leading to redness, itching, and blistering. In severe cases, the blisters can become large and deep, and may even leave scars that are permanently sensitive to light.
The sap can also cause damage to the eyes, leading to conjunctivitis and even blindness if it comes into contact with the eyes. This can happen if the sap splashes into the eyes or if a person rubs their eyes after handling the plant.
It is also important to note that the skin reaction can take up to 48 hours to appear, and the severity of the reaction can depend on the amount of sap that comes into contact with the skin and how sensitive an individual’s skin is.
It is important to take precautions when working with or in the vicinity of giant hogweed. Protective clothing and eye protection should be worn, and the sap should be washed off the skin as quickly as possible. If the sap comes into contact with the skin or eyes, they should be flushed with water immediately and medical attention should be sought.
If you suspect that you have come into contact with Giant hogweed or its sap, it is important to wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and water and to keep the area out of sunlight for 48 hours. If a rash or other symptoms develop, it is important to seek medical attention right away.
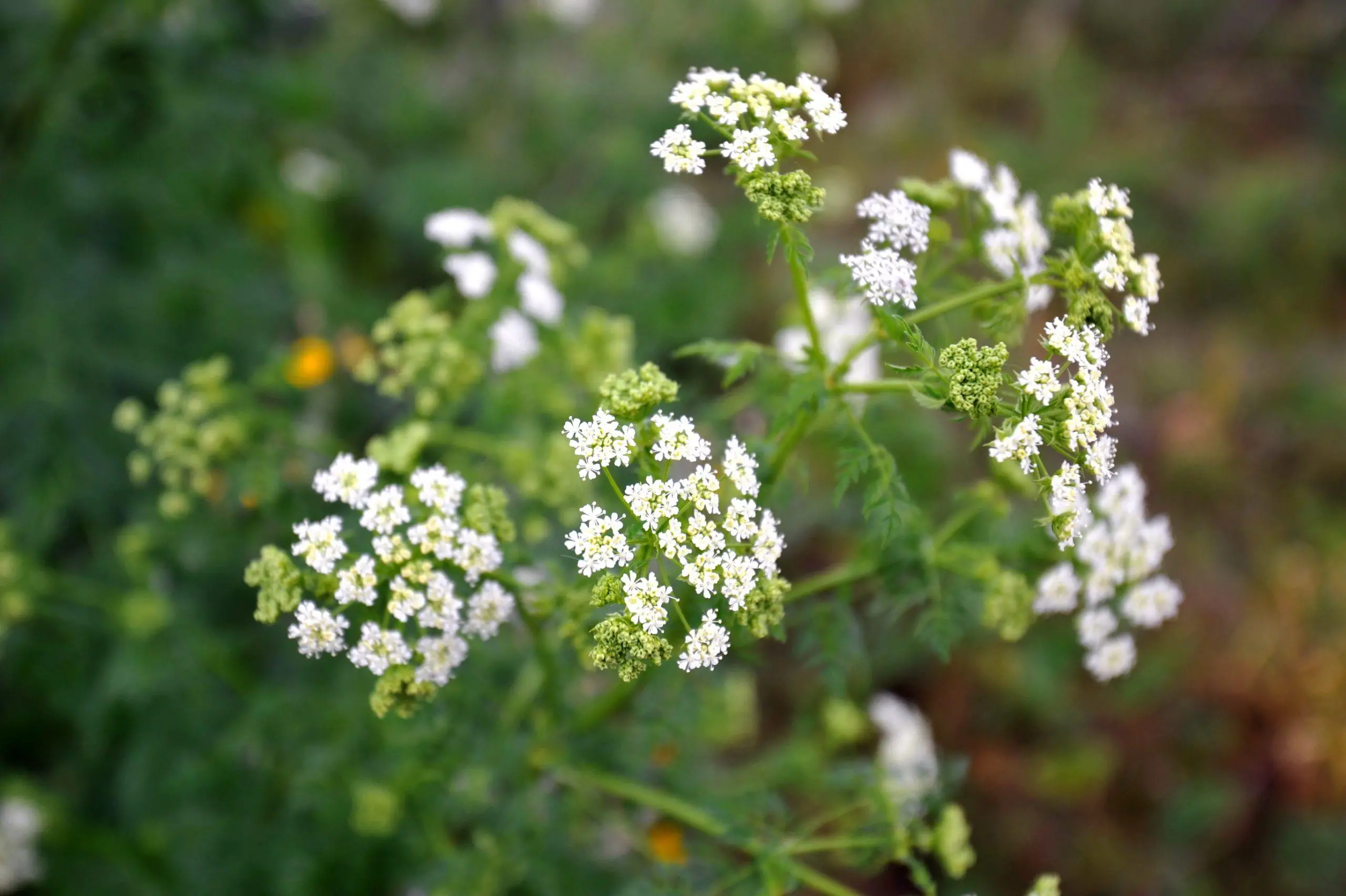

Water hemlock
Water hemlock (Cicuta maculata) is a highly toxic plant that is native to North America. All parts of the plant, including the roots, leaves, and stems, contain a group of toxic compounds called cicutoxins. These compounds can cause severe and potentially life-threatening symptoms when consumed by humans or animals.
Ingesting even small amounts of water hemlock can cause symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and seizures. In more severe cases, the cicutoxins can lead to respiratory failure, coma, and death. The onset of symptoms typically occurs within a few minutes to a few hours after exposure and can last for several days.
One of the most dangerous aspects of water hemlock is that it is often confused with other, non-toxic plants. The leaves of water hemlock are similar in appearance to those of the wild carrot and wild parsnip, and the plant is often found growing near water sources such as streams and wetlands, which can make it even more difficult to identify.
Because of the severe nature of the symptoms caused by water hemlock, it is important to seek immediate medical attention if you suspect that you or someone else may have consumed any part of the plant. Treatment typically involves supportive care such as fluid and electrolyte replacement, as well as medications to control seizures and other symptoms.
In addition to being aware of the dangers of water hemlock and learning to identify the plant, it is also important to take steps to prevent exposure. This may include using caution when foraging for wild plants, keeping children and pets away from areas where water hemlock is known to grow, and properly disposing of any parts of the plant that are removed from your property.
In summary, Water hemlock is a highly toxic plant, in which all parts contain cicutoxins that cause severe symptoms and potential death when ingested by humans or animals. It is important to know how to identify the plant and prevent exposure to it.
Prevention and Treatment
To prevent contact with poisonous weeds, it is important to learn how to identify these plants and to avoid them when spending time outdoors. In addition, it is a good idea to wear long-sleeved shirts, pants, and closed-toe shoes when working in areas where poisonous weeds may be present.
If you do come into contact with a poisonous weed, it is important to wash the affected area with soap and water as soon as possible. Over-the-counter creams and ointments can be used to help relieve the symptoms of a rash, but if symptoms are severe or if you experience difficulty breathing, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
In conclusion
By knowing which weeds are dangerous, you can protect yourself and your family from potential health risks. It is important to take the necessary precautions when working in the yard or garden, such as wearing protective clothing and gloves, washing off any exposed skin after being outside and avoiding contact with known poisonous plants. Taking these simple steps can help keep you safe while enjoying the great outdoors.